Understanding Sand Spreading vs. Die Casting: Which Aluminum Foundry Technique Fits Your Task?
When comparing sand spreading and pass away casting for aluminum tasks, numerous important factors enter into play. Each method has distinct features that deal with different production demands. Recognizing these distinctions can significantly influence project results. As one takes into consideration elements like production volume and style intricacy, the decision ends up being significantly nuanced. Which approach will eventually line up best with details project needs? The response may not be as uncomplicated as it seems.
Summary of Sand Casting
Sand casting is a commonly made use of steel spreading procedure that employs sand as the main mold and mildew product. This method is noteworthy for its adaptability, enabling the production of complicated forms and huge parts. The procedure starts with creating a mold by compacting sand around a pattern, usually made of steel or plastic. When the mold and mildew is ready, liquified metal is poured into the tooth cavity and enabled to solidify. After cooling, the sand mold is escaped to reveal the final casting.
One of the significant advantages of sand casting is its cost-effectiveness, particularly for low to medium production volumes. It fits a range of metals, including aluminum and iron, making it suitable for varied applications. Additionally, sand casting can be adjusted for numerous shapes and sizes, making it possible for suppliers to meet details task demands effectively. This adaptability makes it a preferred selection in sectors such as auto, aerospace, and building and construction.
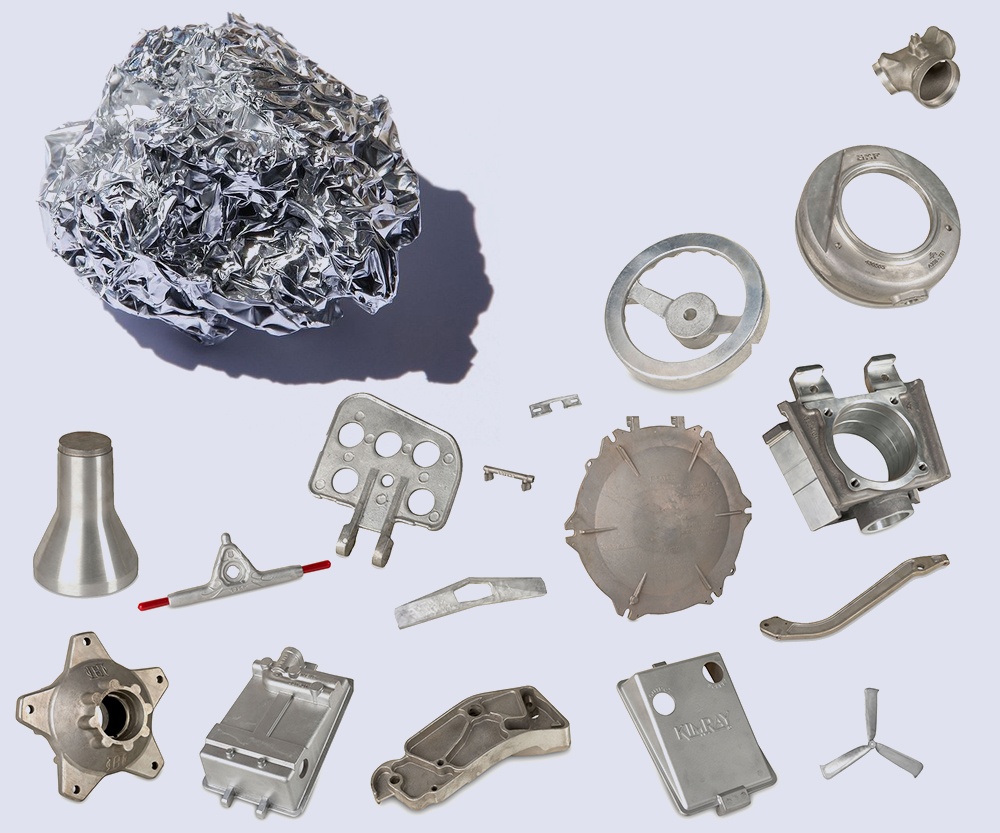
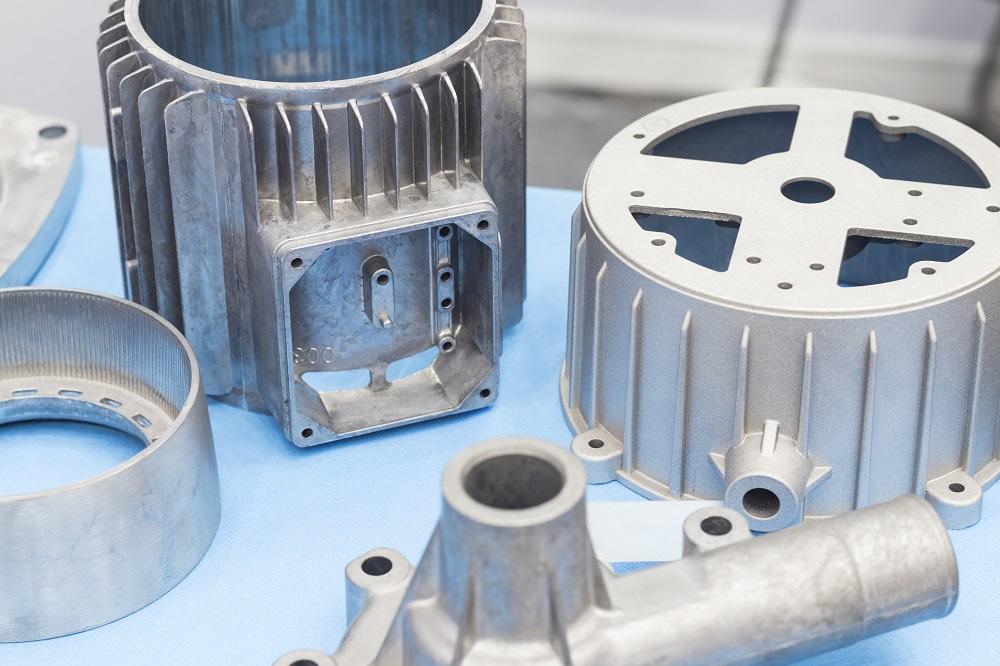
Summary of Die Casting

Secret Benefits of Sand Casting
Among the key benefits of sand spreading depends on its flexibility and cost-effectiveness. This approach fits a wide variety of materials, including numerous aluminum alloys, allowing for varied applications in different markets. The simpleness of the sand spreading process allows suppliers to create complex forms and dimensions without the demand for expensive machining, making it especially advantageous for low to tool manufacturing volumes.
The usage of sand as a mold material supplies excellent thermal properties, helping with the casting of elaborate designs with precision. The capacity to easily create new molds for various try these out tasks better enhances its flexibility. In addition, sand casting needs very little ahead of time financial investment in tooling contrasted to various other casting techniques, making it easily accessible for smaller sized ventures. These benefits jointly position sand casting as a preferred choice for many manufacturers looking for flexibility and economic efficiency in their manufacturing procedures.
Secret Advantages of Die Casting
When comparing casting techniques, die casting offers distinctive benefits that accommodate high-volume manufacturing demands and exact design demands. This method enables the development of complex geometries with tight tolerances, which is vital for markets requiring specific specs, such as automotive and aerospace (Aluminum Casting Company). Pass away casting additionally leads to exceptional surface area finishes, reducing the need for extensive post-processing
The procedure is highly efficient; molten metal is injected into mold and mildews at high pressure, permitting for rapid cycle times and raised production prices. This effectiveness converts into expense savings, making die casting an affordable choice for large-scale production. On top of that, the longevity of elements generated through die casting ensures their long life and reliability in various applications. Inevitably, these advantages setting pass away spreading as a leading option for jobs concentrating on quality, effectiveness, and accuracy in high-volume production scenarios.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Task
Just how can a task supervisor figure out the most ideal casting technique for their specific demands? The decision between sand spreading and die casting depend upon several crucial aspects. First, the task manager must assess the required volume of parts; pass away casting is more effective for high-volume production, while sand casting fits low to modest quantities. Next off, they ought to take into consideration the intricacy of the style. Elaborate geometries commonly prefer die spreading because of its accuracy capabilities, whereas sand casting enables for higher versatility in style adjustments.
Material properties additionally play an essential function, as die spreading typically generates stronger components with premium surface finishes. Expense implications, consisting of tooling and product costs, should be assessed; sand casting usually provides reduced first prices yet can be less effective in automation. Ultimately, the task manager need to weigh these variables against task timelines, budget restraints, and high quality demands to pick the ideal approach that aligns with the project's objectives.
Regularly Asked Concerns
What Types of Light Weight Aluminum Alloys Appropriate for Sand and Die Casting?
Numerous light weight aluminum check my reference alloys are ideal for sand and die casting, including 356, 319, and 413 alloys. These selections are preferred for their excellent castability, mechanical homes, and viability for diverse applications in manufacturing.
How Do Production Costs Contrast Between Sand Spreading and Die Casting?
Production expenses for sand casting are usually reduced because of simpler products and configurations. In contrast, die spreading involves greater preliminary expenditures from tooling yet offers price savings via automation, making it much more cost-effective at larger ranges.
Can Both Approaches Create Facility Geometries?
What Is the Regular Preparation for every Casting Technique?
Commonly, sand spreading preparation vary from one to 3 weeks, influenced by intricacy and volume. In contrast, die casting typically offers quicker manufacturing, with preparations commonly in between one to 2 weeks, depending upon layout requirements.
Just How Do Ecological Aspects Impact Casting High Quality?
Environmental elements, including dust, temperature level, and humidity degrees, greatly influence casting high quality. Variations can result in flaws such as porosity or surface imperfections, inevitably influencing the mechanical residential or commercial properties and efficiency of the last cast item.
When comparing sand spreading and pass away casting for aluminum projects, several crucial factors come into play (Aluminum Foundry). Sand casting is a commonly made use of metal casting process that uses sand as the investigate this site main mold and mildew material. Pass away casting is one more prominent metal spreading process that offers distinctive benefits contrasted to sand spreading. The task manager should evaluate the required quantity of components; die casting is a lot more effective for high-volume manufacturing, while sand casting suits reduced to moderate quantities. Both sand spreading and pass away spreading can produce complex geometries, though they achieve this in different ways